Theme: Recent advancements in Medical Microbiology
Medical Microbiology 2022
We warmly invite participants from across the world to the “11th Global Medical Microbiology Summit & Expo” which is organised to be held on November 02-03, 2022 at Rome, Italy This summit provides an opportunity to connect and establish a global network between Medical experts, Doctors, Microbiologists, epidemilogists, pharmaceuticals, biotechnologists, food technologists & industrialists for disscussions related to current challenges and latest research in the field of medical microbiology as well as for the future collaborations and partnerships. The highlights of the summit will be key note presentations, poster presentations, oral talks (speaker forum and young research forum), exhibitions, workshops and video presentations.
Why to attend?
It's a great chance to network with medical professionals, microbiology experts, food microbiology societies, biotechnologists, epidemiologists, and pharmaceutical associations. The summit provides a global forum for the exchange of fresh scientific knowledge on microbiological research and development, as well as the efficacy of various regulatory programmes in this field.
Target Audience
Immunologists|MedicalExperts|Epidemiologists|MedicalExperts|Pathologists|Bacteriologists|virologists|geneticengineers | medical device | industrialists| Epidemologists | Pathologists | Bacteriologists | virologists | geneticengineers | medical device | industrialists | cellular microbiologists |hospitals | laboratories and associations | Doctors |Microbiologists | Food microbiologists | Academicians | Students (post graduates, doctorates) | Pharmacists | Microbiology societies | Medical Microbiology societies | Individuals involved in medical microbiology | industrial microbiology | biotechnology.
Track 1: Microbiology Research and Advancements
In medical microbiology, rapid identification of microorganisms can be extremely useful in determining the best patient management options for diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, mycobacteria, and parasites. Rapid detection of microorganisms in clinical samples allows for a smooth transition from broad-spectrum to focused antibiotic therapy. Antibiotic hazards, including as disruption of natural flora, toxic side effects, and selective pressure, are reduced when patients move to customised therapy. New tools in clinical microbiology are desperately needed, especially for bloodstream infections, which have one of the highest fatality rates of all illnesses. In addition, the clinical laboratory community must embrace evidence-based interventional laboratory medicine procedures and engage in translational research projects to demonstrate clinical usefulness.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 2: Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes are an essential part of life on the planet. Not all microorganisms are harmful. Many bacteria are extremely beneficial to humans. Almost every day, we employ bacteria and microbially produced goods. Antibiotics have made a significant contribution to the control of infectious diseases such as diphtheria, whooping cough, and pneumonia. Microbes benefit humans in a variety of ways, including vaccines and antibiotics, as well as household products such as Lactobacillus, a bacterium found in curd. Sewage Treatment - Bacteria like Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter are engaged in sewage fermentation. One of the bacteria involved in the degradation of organic substances is Pseudomonas. Gobar Gas Production- Methanobacterium produces gobar gas anaerobically. During recombinant DNA technology, viruses are used as a vector for transmitting the needed gene.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 3: Microbial Vaccines
A vaccination is a biological preparation that boosts your immune system against a certain disease. A vaccination usually comprises an agent that looks like a disease-causing bacteria, and it's usually created from weakened or destroyed versions of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The agent induces the immune system to recognise the agent as foreign, destroy it, and remember it so that the immune system can recognise and destroy any of these germs it encounters later.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 4: Infection Prevention and Control
In order to avoid the spread of communicable diseases, infection prevention and control are essential in all health care settings. Infection prevention and control necessitates a basic awareness of disease epidemiology, risk factors that increase patient susceptibility to infection, and infection-causing activities, procedures, and therapies. The mechanism of transmission of the infectious agent, the type of patient-care activity or operation being performed, and the underlying patient's host defences all influence the likelihood of contracting a health-care-associated infection. The greatest approach to protect yourself and others from infectious diseases is to get vaccinated.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 5: Infection and Immunity
Immunology is a discipline of science that studies the immune system, including both innate and acquired immunity, as well as laboratory techniques involving the interaction of antigens with specific antibodies. Microbiology is a discipline of science that studies different microorganisms. Microbiology is the study of bacteria's structure and numerous physical, chemical, and biological features that relate to their disease-causing potential. The process of recognising which disease or condition causes a person's symptoms and indicators is known as medical diagnosis. Laboratory tests can either directly identify organisms (e.g., by looking at them, using a microscope, or growing them in culture) or indirectly identify organisms (e.g., by looking at them, using a microscope, or growing them in culture) (e.g., identifying antibodies to the organism). Microscopy, culture, and immunologic tests (agglutination tests such as latex agglutination) are examples of common types of tests.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 6: Pathogenicity of Microbes
The ability of an organism to cause disease is referred to as pathogenicity (ie, harm the host). The overt damage done to the host is a function of the host-pathogen interactions, and this ability represents a genetic component of the pathogen. This innate propensity to cause disease is absent in commensals and opportunistic pathogens. Disease, on the other hand, is not always the result of the host-pathogen interaction, and pathogens can exhibit a wide spectrum of virulence. The degree of pathology caused by the organism is referred to as virulence, a term that is typically used interchangeably with pathogenicity. The pathogen's ability to reproduce within the host is usually connected with its virulence, although it can also be influenced by other factors. The progression of a disease is a dynamic process.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 7: Agricultural Microbiology
Plant-associated microorganisms are the focus of agricultural microbiology research. Its goal is to address issues in agricultural practises that are typically caused by a lack of biodiversity in microbial populations. Understanding microbial strains that are relevant to agricultural applications can help improve soil nutrients, plant-pathogen resistance, crop robustness, fertiliser uptake efficiency, and other variables. The numerous symbiotic interactions between plants and bacteria can eventually be harnessed for increased food production to feed the growing human population, as well as safer agricultural approaches to minimise ecological impact.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 8: Antimicrobial Agents and Infectious diseases
Antimicrobials are agents that kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. They are classified as antibacterials, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitics. Antibacterials are used to treat bacterial infections, antivirals are used to treat viruses, and antifungals and antiparasitics are used to treat fungus and parasites, respectively. Antibacterials have a relatively low toxicity to humans and other animals. Antimicrobial pesticides utilise disinfection, sanitation, or development inhibition to prevent contamination and spoilage caused by bacteria, viruses, fungus, protozoa, and algae in industrial processes or systems, surfaces, water, or other chemical substances.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 9: Pharmaceutical Microbiology
Pharmaceutical microbiology is concerned with the study of microorganisms used in the production of prescription medications. Other aspects of pharmaceutical biological science include the research and development of anti-infective agents, the use of microorganisms to detect agent and malignant neoplastic disease activity in future medications, and the use of microorganisms in the production of pharmaceutical products such as endocrine and human growth hormone.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 10: Public Health Microbiology and Emerging Infectious Diseases
Microbial pathogenesis, public health principles, epidemiology, molecular genetics, virology, and environmental and industrial microbial activities are all covered in the Public Health and Microbiology concentration. This focus prepares students for technical work or graduate study in microbial disease systems using polymerase chain reaction, other molecular diagnostic methods, and environmental and industrial microbial applications.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 11: Medical Microbiology
Medical microbiology is an area of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of infectious and non-infectious disorders. Clinical consultations on the investigation, principles of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of infectious diseases; the scientific development, administrative, and medical direction of a clinical microbiology laboratory; the establishment and direction of infection control programmes across the continuum of care; and communicable disease prevention and epidemiology, as well as related public health issues are all things that medical microbiologists deal with.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 12: Microbial Enzymes
Enzymes have been proposed as a biocatalyst for a variety of processes. Microbial enzymes, in particular, are widely used in industry and health. Plant and animal enzymes are less active and stable than microbial enzymes. Furthermore, due to their biochemical diversity and susceptibility to gene manipulation, microorganisms represent an alternative source of enzymes because they can be cultured in large quantities in a short time using fermentation and because they can be cultured in large quantities in a short time using fermentation. Industries are looking for new microbial strains that can manufacture a variety of enzymes to meet existing enzyme demands
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 13: Microbial Biofilms
Cells that are typically contained inside a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) cling to one other and/or to a surface in a microbe aggregate. A biofilm is a system in which the occupants may adapt to changing environmental circumstances internally. Slime, or self-produced extracellular polymeric material, is a polymeric aggregation made up of extracellular biopolymers in diverse structural configurations.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 14: Marine Microbiology
Microorganisms (bacteria, archaea, viruses, and microbial eukaryotes) in the marine environment, including their biodiversity, ecology, and biogeochemistry, are studied in marine microbiology. Met genomics has played a critical role in determining the quantity and character of marine microbial ecosystems.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 15: Biofuel
Biofuel is an energy source derived from live organisms or the waste produced by living organisms. Biofuel supporters say that its use might significantly reduce greenhouse emissions because, unlike burning fossil fuels, growing plants or biomass removes carbon dioxide from the environment. A biofuel is a fuel produced by modern biological processes, such as agriculture and anaerobic digestion, rather than geologic processes, such as those involved in the creation of fossil fuels, such as coal and crude oil, from prehistoric organic matter.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 16: Molecular Microbiology
The discipline of microbiology dedicated to the study of the molecular basis of physiological activities in microbes is known as molecular microbiology. It is concerned with germs' molecular mechanisms and physiological activities, as well as their use in the development of biotechnology goods and medications such as vaccines and antibodies. It also includes advancements in microbial pathogenicity.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 17: Public health microbiology
Microorganisms that can be dangerous or useful to human health are studied in public health microbiology, a branch of microbiology. Medical microbiology conferences have always had a strong presence on the subject. Medical microbiology is concerned with pathogenic bacteria, hence studying germs for public health is an essential problem.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 18: Predictive microbiology
Predictive microbiology is a discipline of microbiology that deals with the mathematical or quantitative examination of factors that influence microbes' chemical, reproductive, and physical behaviour. Because each microorganism's response varies depending on the environment, the study aids in predicting the survival rate and response of those microorganisms in various settings.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 19: Microbial epidemiology
The study of the occurrence, distribution, frequency, and variables that cause disease to spread in a given population is known as epidemiology. S. typhi, SARS virus, and protozoans are the most prevalent microbes that cause epidemics.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 20: Virology , Viral pathogens & Associated Diseases
Virology is a branch of microbiology or medicine that studies new and reemerging viruses that cause serious and/or fatal diseases in people and animals. Filoviruses (Ebola, Marburg), henipaviruses (Nipah, Hendra), Lassa virus, Lujo virus, South American hemorrhagic fever viruses (Junin, Machupo, Guanarito, Chapare, Sabia), Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, Rift Valley fever virus, hantaviruses, SARS coronavirus, MERS coronavirus
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 21: Clinical Infections & Vaccines
The most up-to-date information on common healthcare-associated illnesses will be presented, including Clostridium difficile, pneumonia, and severe urinary tract infections. This track's study aims to combine angstrom-level discovery with clinical research in order to lessen the global burden of infectious illnesses.
1. Clinical Trials and Diseases Caused by Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Prions, or Parasites, including Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Prions, or Parasites
2. Clinical Epidemiology and Infection Prevention and Control: Healthcare-Associated and Surgical Infections
3. International Health
4. Infectious Diseases in Transplant Patients
5. Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents
6. Science of Vaccines and Immunization
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 22: Antimicrobial agents & Resistance
The rising tide of antimicrobial resistance, with the advent of "untreatable" microorganisms producing diseases that were once easily treated, is one of our biggest health challenges today. Find out about the discovery of novel antimicrobial agents, preclinical studies of new antimicrobial medications in development, and first-look data from human clinical trials using new antimicrobial agents.
1. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance: Molecular Typing, Clinical, and Molecular Epidemiology
2. Antimicrobial Agents: Action Mechanisms and Resistance Mechanisms
Antifungal Agents and Resistance to Antifungal Agents
4. Antiviral Agents and Resistance (Including HIV Drugs)
5. Antimicrobial stewardship, including the provision of high-quality care
Therapies, diagnostics, and drug discovery are all examples of novel approaches.
7. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and General Pharmacology in Antimicrobials
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
Track 23: Environmental Microbiology
The study of the composition and physiology of microbial communities in the environment is known as environmental microbiology. Environmental microbiology originated as a rather obscure field of the Life Sciences, but has since evolved into one of the most dynamic and visible areas of contemporary research. Environmental microbiology interacts with several different areas, including soil, aquatic, and water quality, bioremediation, occupational health and infection control, food safety, and industrial microbiology, because environmental microbes affect many aspects of life and can easily be transported between environments.
Recommended Microbiology Conferences | Infectious Diseases Conference | International Microbiology Conference
Related : Societies
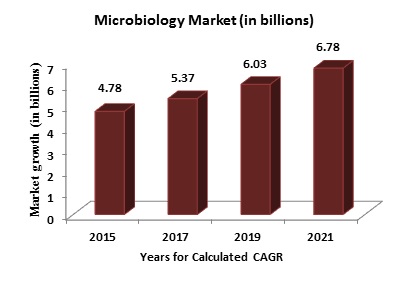
Global Market analysis of microbiology 2015 - Forecasts to 2024
In 2015, the global clinical microbiology market was worth USD 8.4 billion, and by 2024, it is predicted to be worth USD 16.1 billion. The ongoing development of new products, together with rising demand in pharmaceutical and clinical applications for the study and detection of various infectious diseases, are key factors driving market expansion.
The global clinical microbiology market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5 percent over the forecast period, from USD 3.9 billion in 2020 to USD 5.3 billion in 2025. For both established and new product producers, the global microbiological testing/clinical microbiology market has substantial growth potential. Some of the important drivers driving the growth of the microbiological testing/clinical microbiology market include technological advancements, rising frequency of infectious diseases and epidemic outbreaks (such as COVID-19), higher financing, and public-private partnerships.
The clinical microbiology market has been split by product, application, disease, and geography, according to research. One of the key causes driving the adoption of clinical microbiology in the healthcare industry for illness diagnosis and monitoring is the growing elderly population and, as a result, the rising prevalence of infectious diseases. Furthermore, the industry is gaining traction with the introduction of cutting-edge devices such as the MALDI Biotyper, GeneXpert, and Myla IT performance management systems.
Conference Highlights
- Microbiology Research and Advancements
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Microbial Vaccines
- Infection Prevention and Control
- Infection and Immunity
- Pathogenicity of Microbes
- Agricultural Microbiology
- Antimicrobial Agents and Infectious diseases
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology
- Public Health Microbiology and Emerging Infectious Diseases
- Medical Microbiology
- Microbial Enzymes
- Microbial Biofilms
- Marine Microbiology
- Microbes and Biofuels
- Molecular Microbiology
- Public health microbiology
- Pharmaceutical microbiology
- Predictive microbiology
- Microbial epidemiology
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 02-03, 2022 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Medical Microbiology & Diagnosis
- Journal of Food & Industrial Microbiology
- Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by





